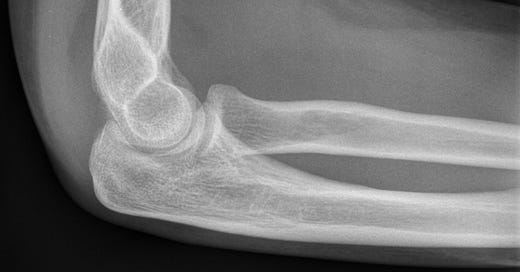
Radial head fractures typically result from falls onto an outstretched arm/hand with axial forces transmitted along the radius. Most fractures are subtle and may be impacted or intra-articular. Patients present with lateral elbow pain upon passive forearm pronation and supination. In the setting of acute trauma, a joint effusion, even if there is no cortical disruption or contour deformity, indicates a nondisplaced radial head fracture. Findings include an elevated anterior elbow fat pad (sail sign) and/or a visible posterior olecranon fat pad.
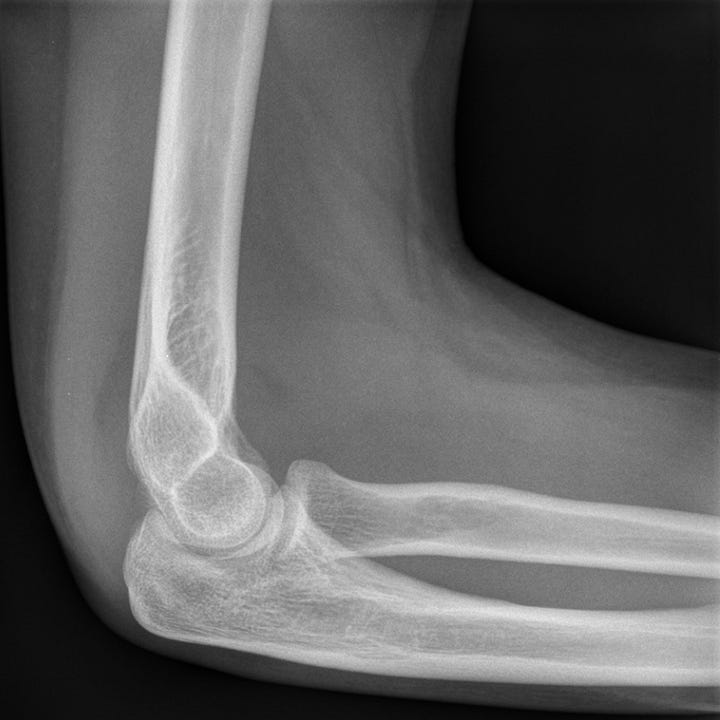
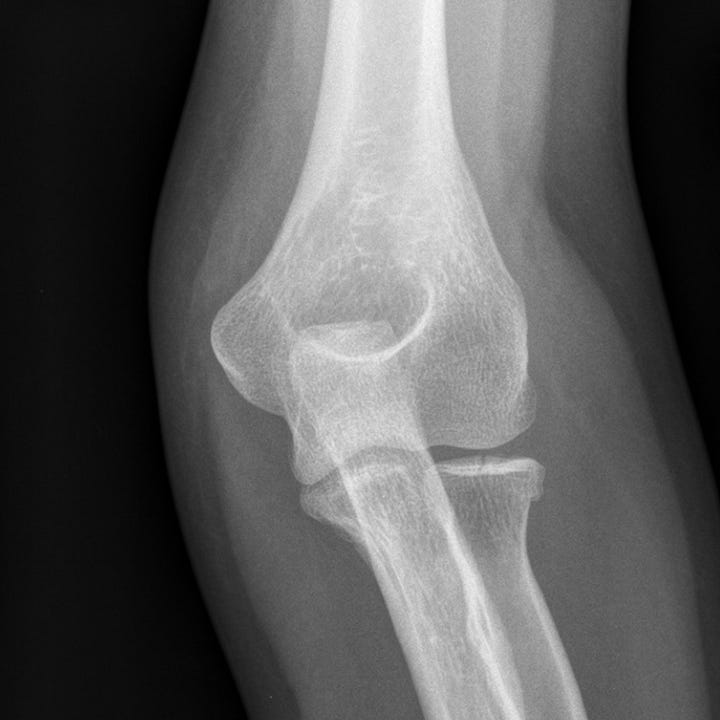
Intra-articular radial head fracture. Nondisplaced, mildly impacted, intra-articular radial head fracture. Elevation of the anterior and visible posterior elbow fat pads indicate elbow effusion. The ulna and distal humerus are normal.
Associated injuries may include ulnar coronoid process fracture, elbow dislocation, medial collateral ligament injury, interosseous membrane injury, and damage to the wrist triangular fibrocartilage complex.
Radial head fracture classification (Mason)
Type I
Non-displaced fracture
Type II
Partial fracture with > 2 mm displacement (impaction, depression, angulation)
Type III
Comminuted fracture of entire radial head
Type IV
Comminuted fracture with associated elbow dislocation
Type I fractures are treated conservatively with brief immobilization and analgesia. Type II fractures are treated with open reduction and internal fixation. Type III fractures of-ten require excision of the radial head and prosthetic replacement.
The Essex-Lopresti fracture-dislocation is defined by interosseous ligament disruption, usually accompanied by a fracture of the radial head and disruption of the wrist triangular fibrocartilage. These injuries result in distal radioulnar joint dislocation; associated clinical findings include pain in the wrist and forearm on pronation and supination, and swelling and tenderness over the fractured radial head. Treatment consists of radial head repair or replacement.
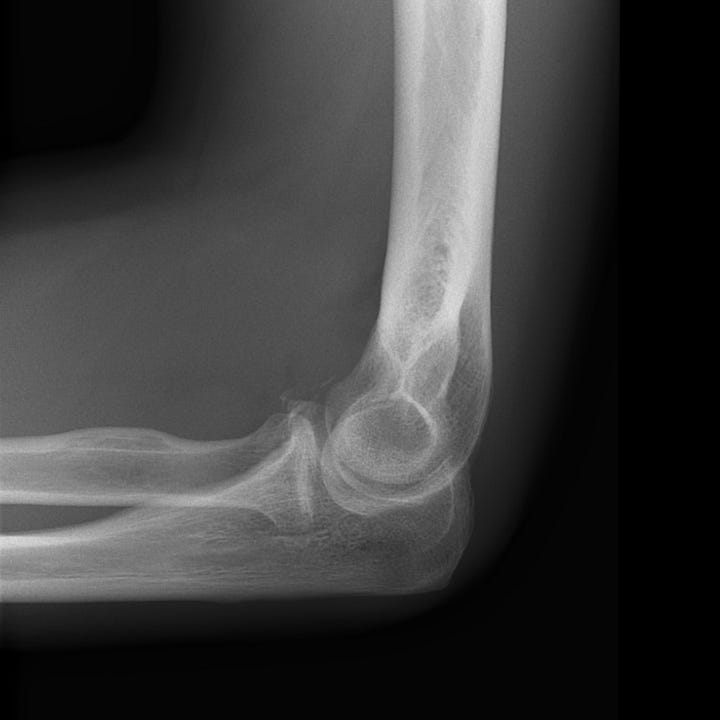
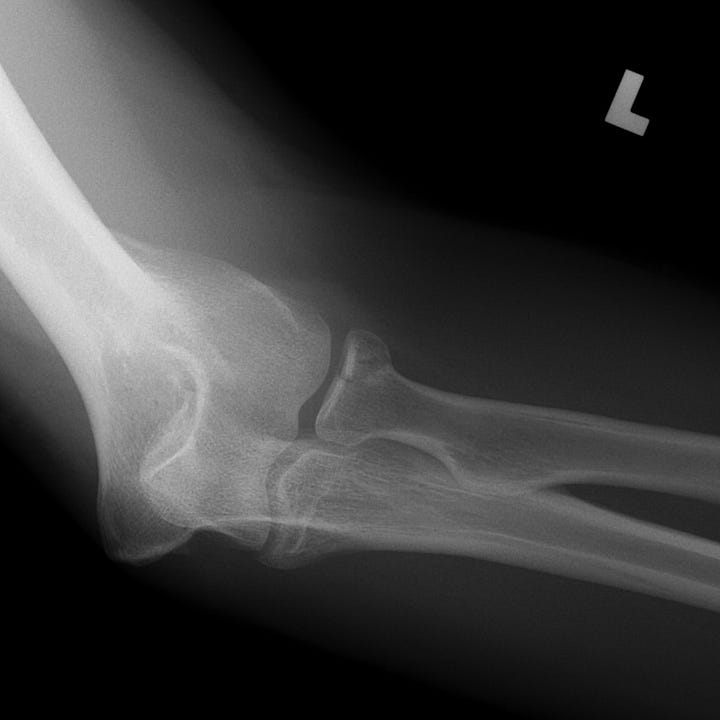
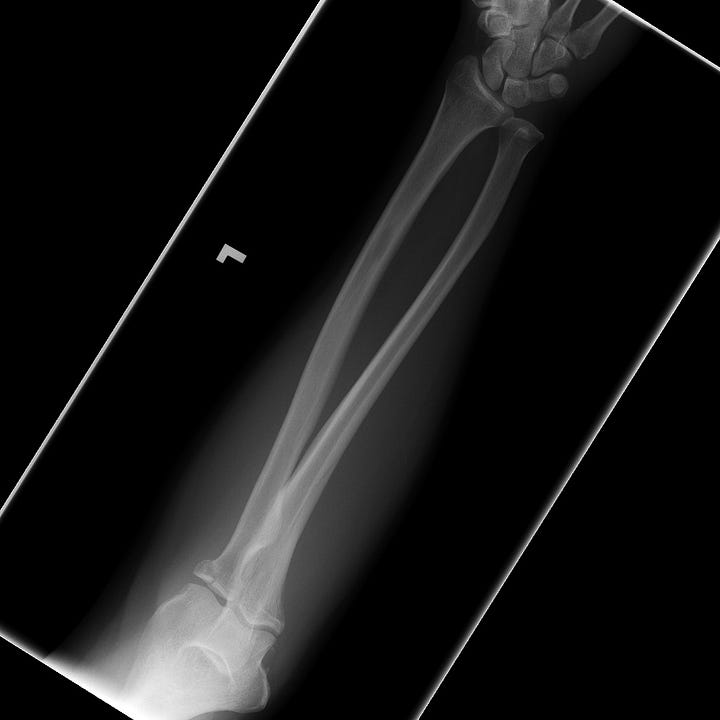
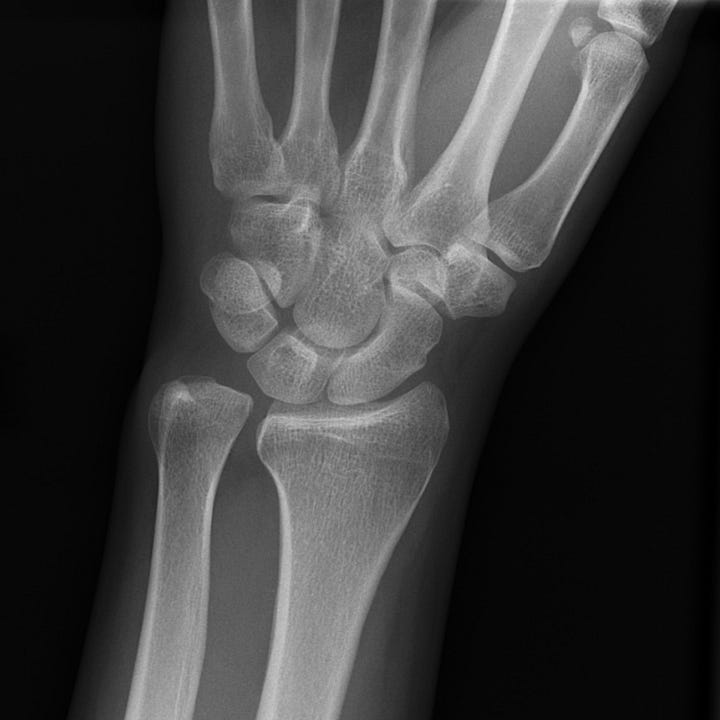
Essex-Lopresti fracture-dislocation. Impacted intra-articular radial head fracture with associated widening of the distal radioulnar articulation and subluxation of the distal ulna.