Midface smash injury is a general term for any severely comminuted, high-energy impact, facial fracture pattern that is not easily categorized as a Le Fort, zygomaticomaxilary complex, or naso-orbito-ethmoid fracture. They can be loosely classified based on the their location as frontal, nasofrontal, or central, but these categories typically overlap.
Frontal midface smash injuries are characterized by disruption of the frontal sinus; nasofrontal injuries involve the orbits, orbital apices, and ethmoidal roof, and central smash injuries involve the orbits, maxilla, and mandible.
CT shows extensive facial bone comminution, often with posterior fragment displacement. Nonosseous structures that can be injured include upper cranial nerves, globes, extraocular muscles, nasolacrimal ducts, and sinuses.
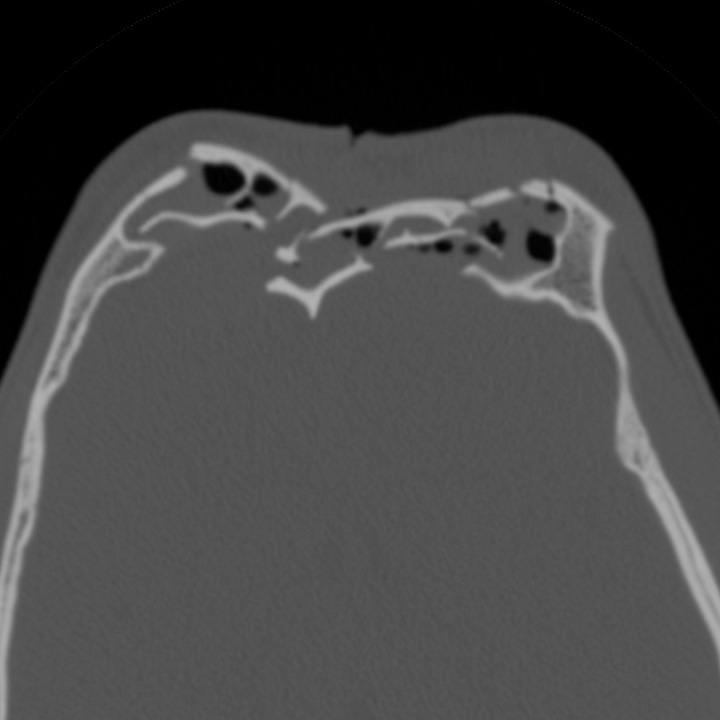
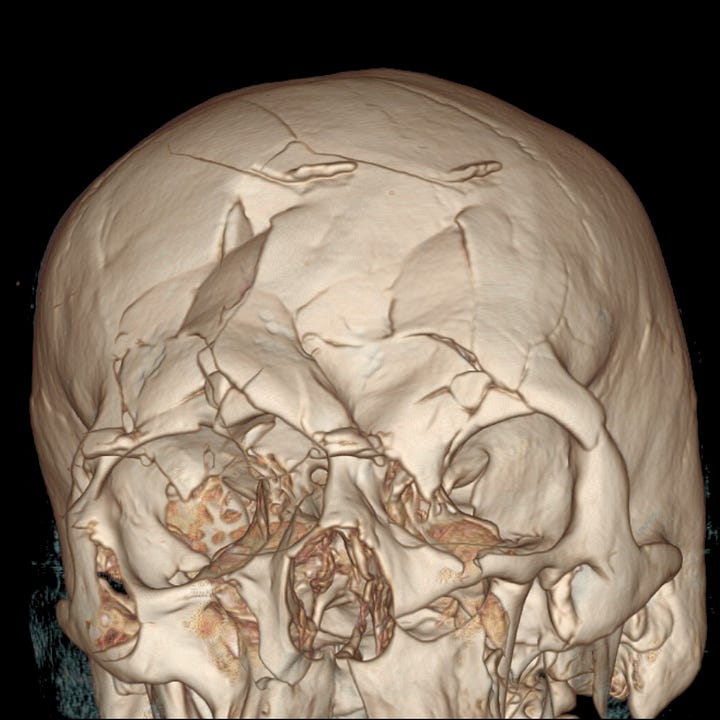
Frontal type midface smash. Severely comminuted fracture, predominantly involving the frontal sinus, but with associated orbital wall and maxillary fractures.
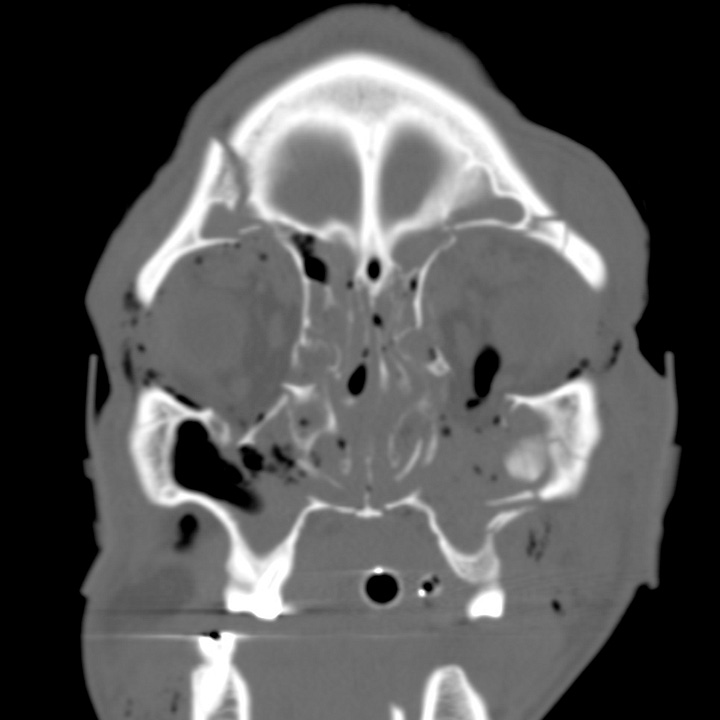
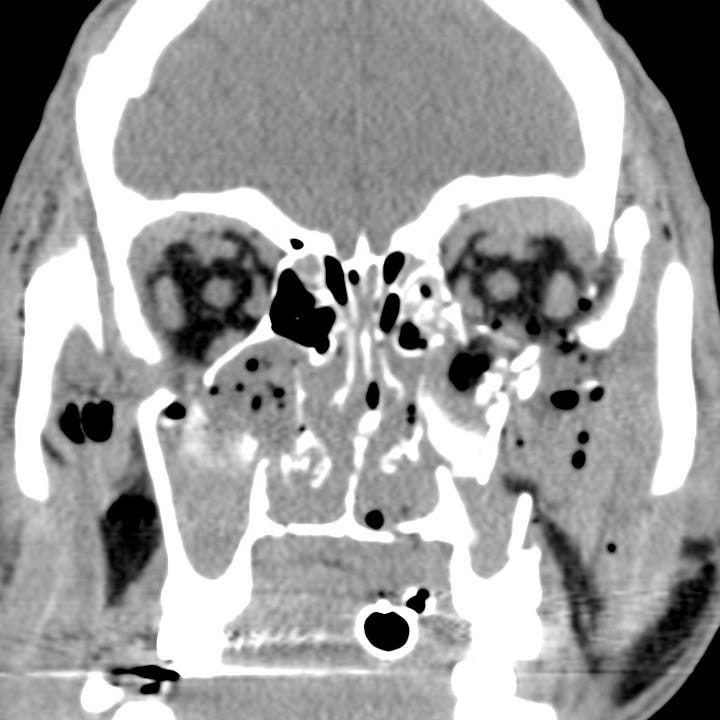
Nasofrontal type. Comminuted nasal bone, orbital roof, orbital floor, and frontal bone fractures. Bilateral superior orbital extraconal hematomas. Extensive soft tissue emphysema.
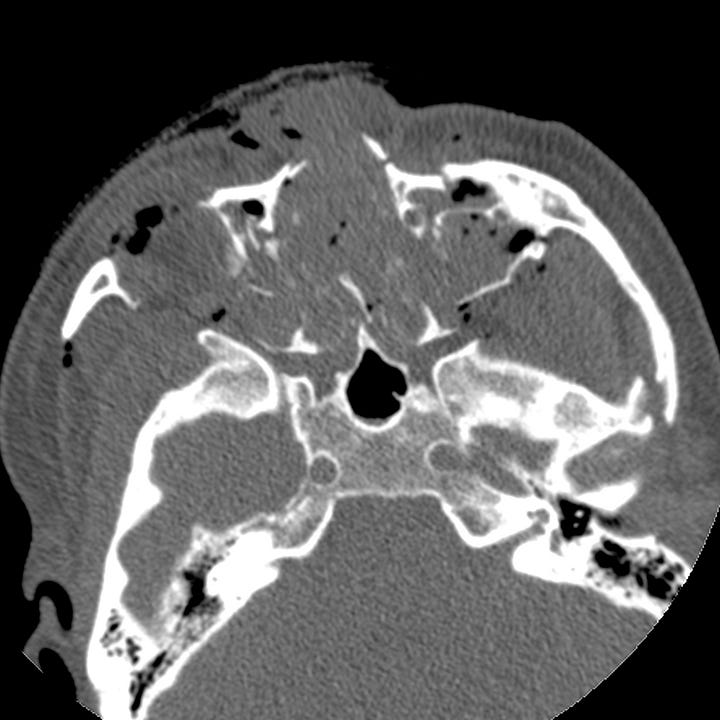
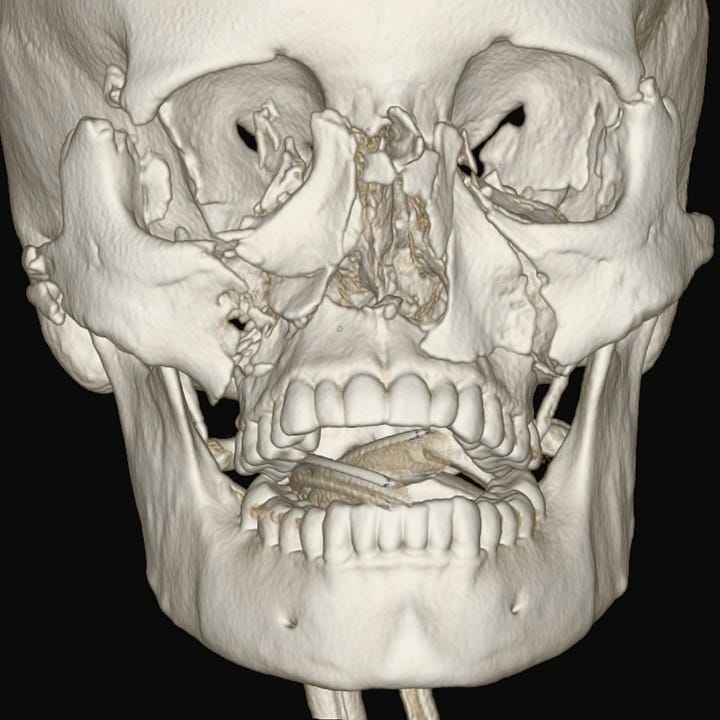
Central smash type. Nasal, maxillary, and lateral orbital wall fractures.


