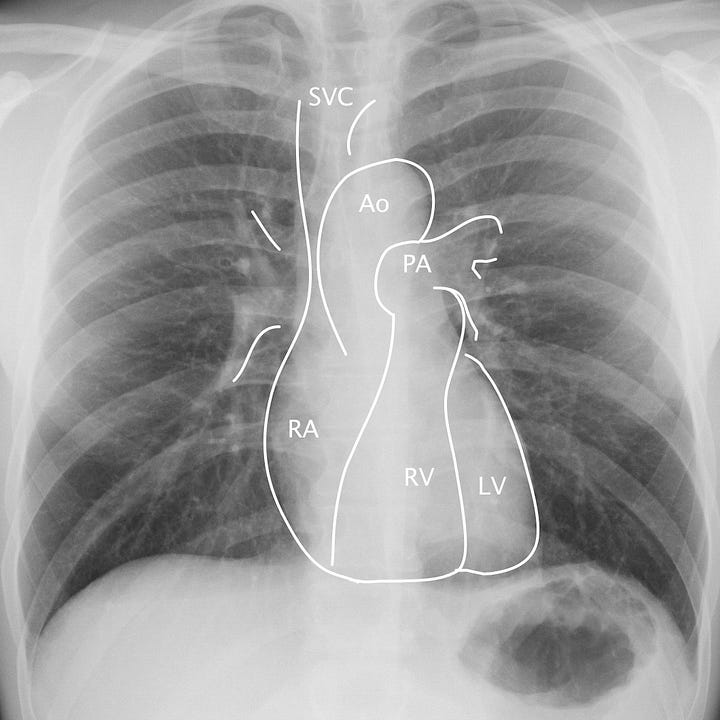
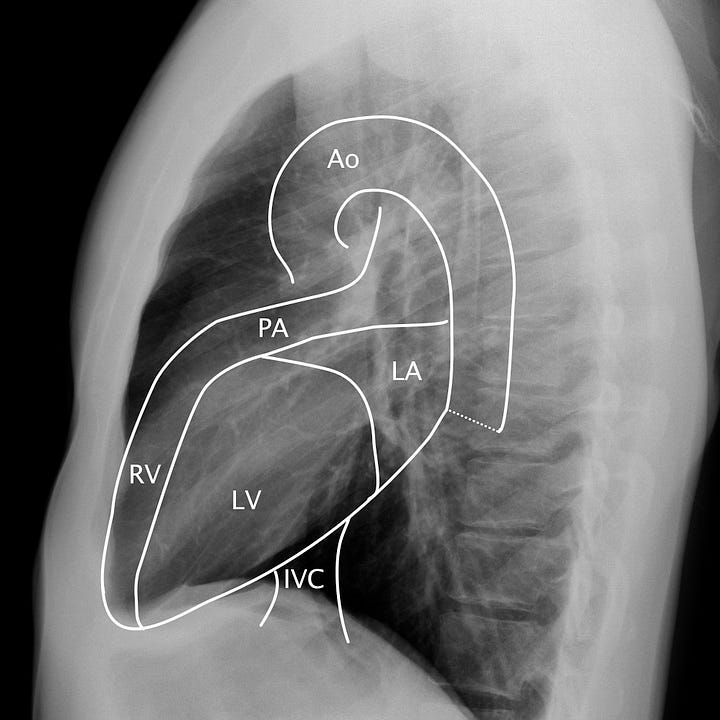
Cardiomediastinal anatomy. On the frontal radiograph, the right heart border corresponds to the right atrium (RA) and superior vena cava/right atrial junction. The left heart border corresponds to the left ventricle (LV). On the lateral radiograph, the anterior border of the heart is made up of the right ventricle (RV) and pulmonary outflow tract (PA), with the inferior and posterior margins formed by the left ventricle, inferior vena cava (IVC), and left atrium (LA). The retrosternal space in adults should be free of soft tissue.
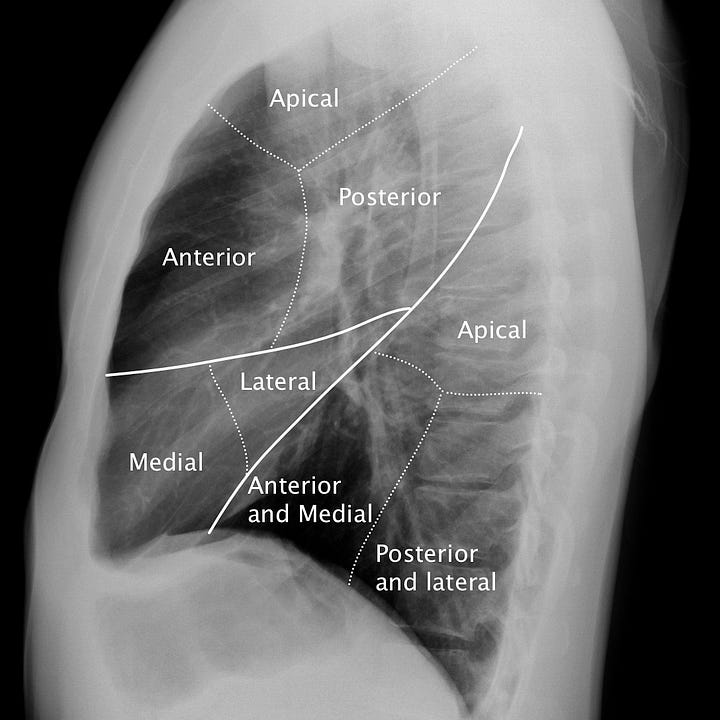
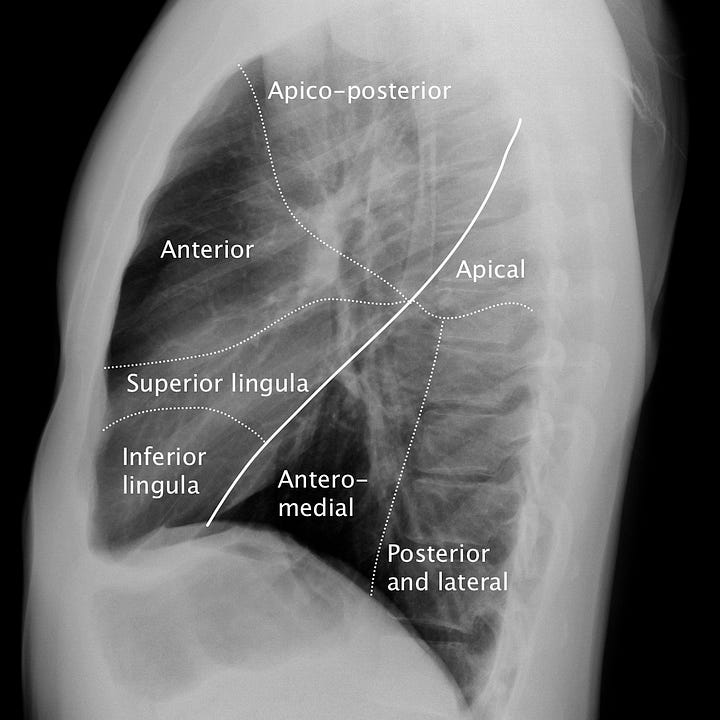
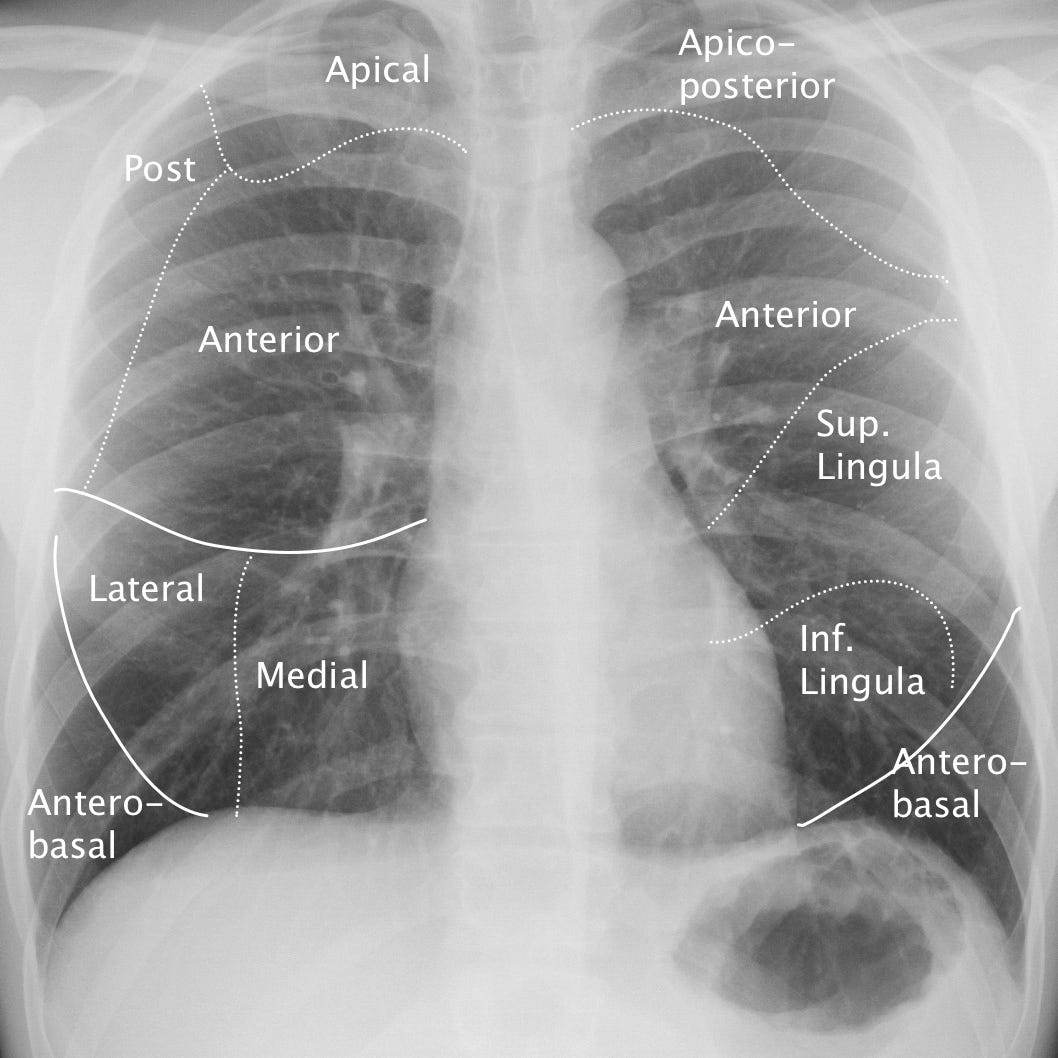
Pulmonary segmental anatomy. The lobar anatomy of the right and left lungs dif- fers; the right lung contains a middle lobe and the left upper lobe contains a roughly analogous lingular segment. On the lateral radiograph, the right and left lungs are superimposed upon each other. Localizing an intrapulmonary mass or lesion requires attention to both frontal and lateral views.
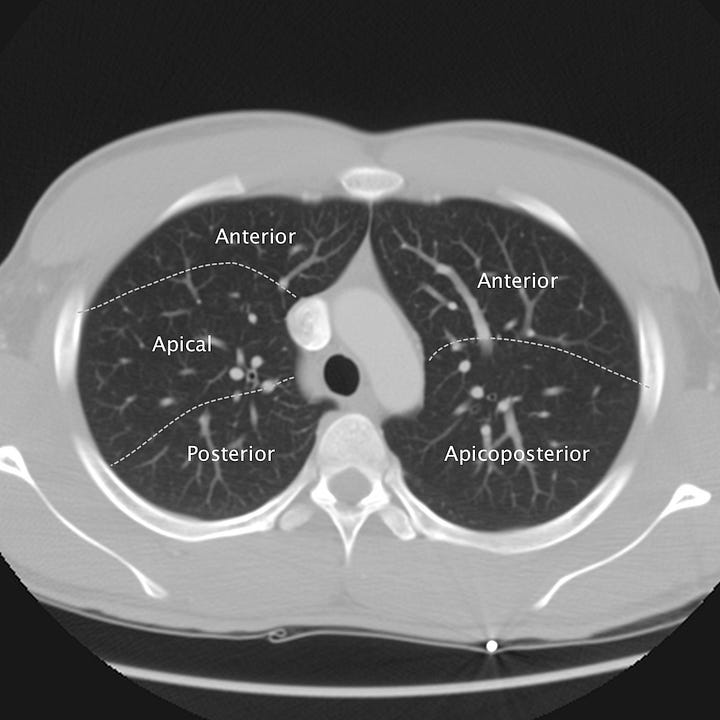
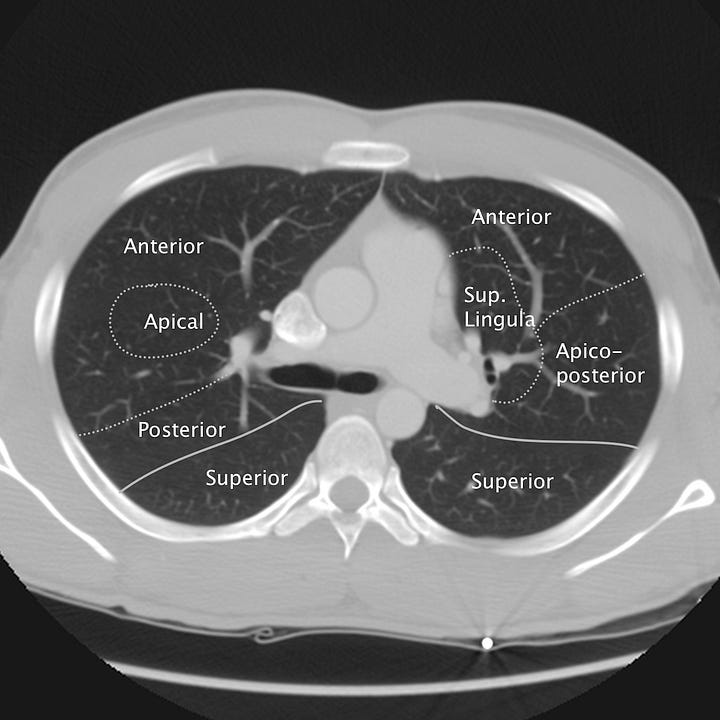
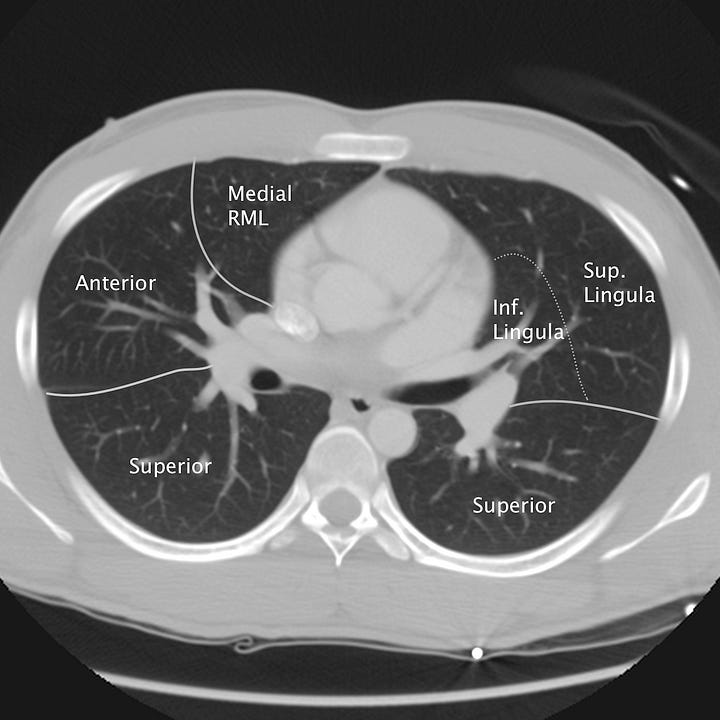

Pulmonary segmental anatomy on CT. Axial images at the levels of the Aortic arch, pulmonary artery, aortic root/left mainstem bronchus, and cardiac chambers. Solid lines denote lobar divisions. Dotted lines indicate segmental borders.
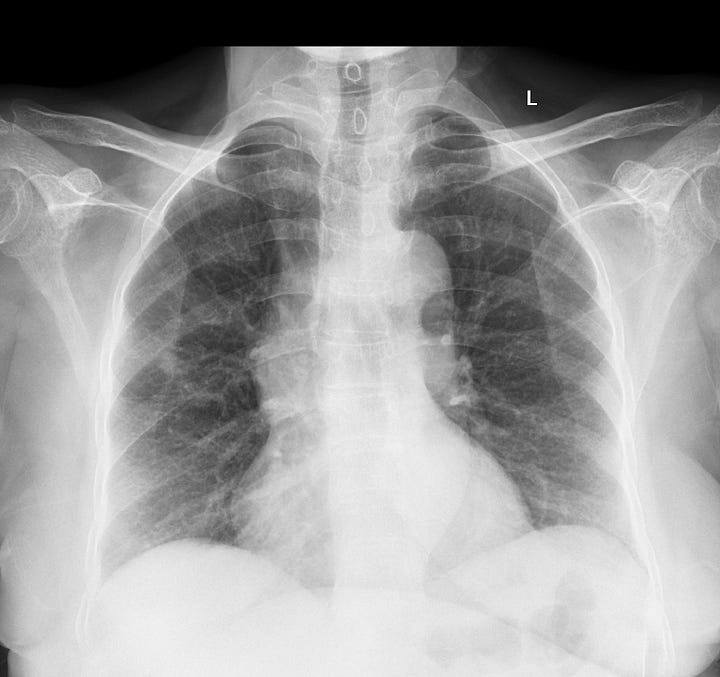

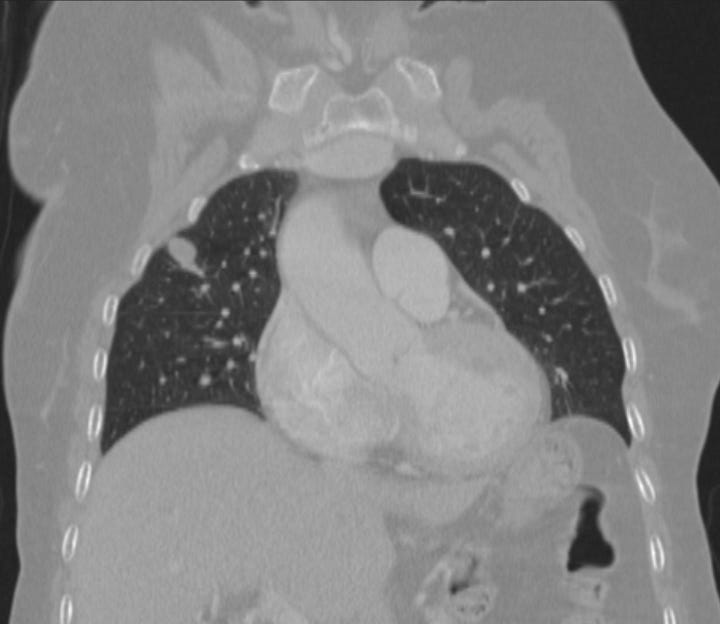
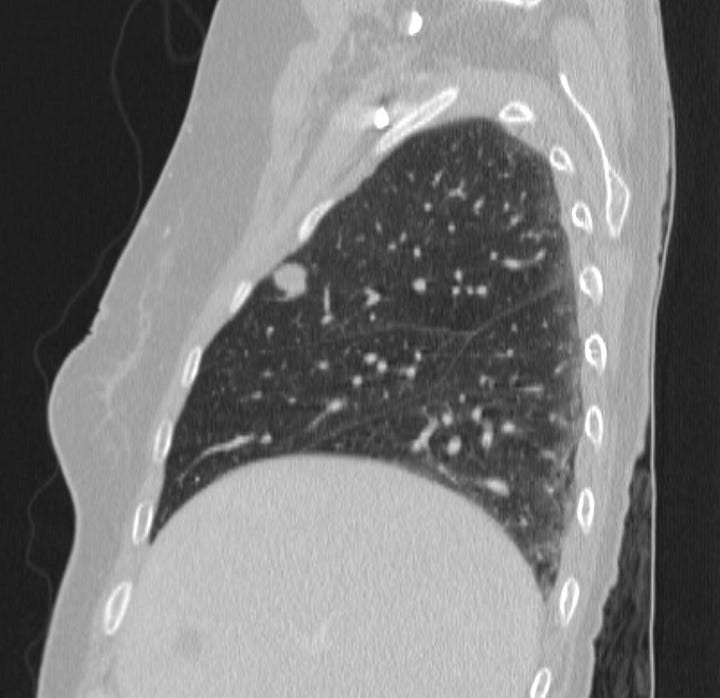
Localization of incidental pulmonary nodule. A 1 cm nodule located between the 5th and 6th posterior ribs on the frontal radiograph is located in the anterior segment of the right upper lobe.