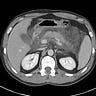
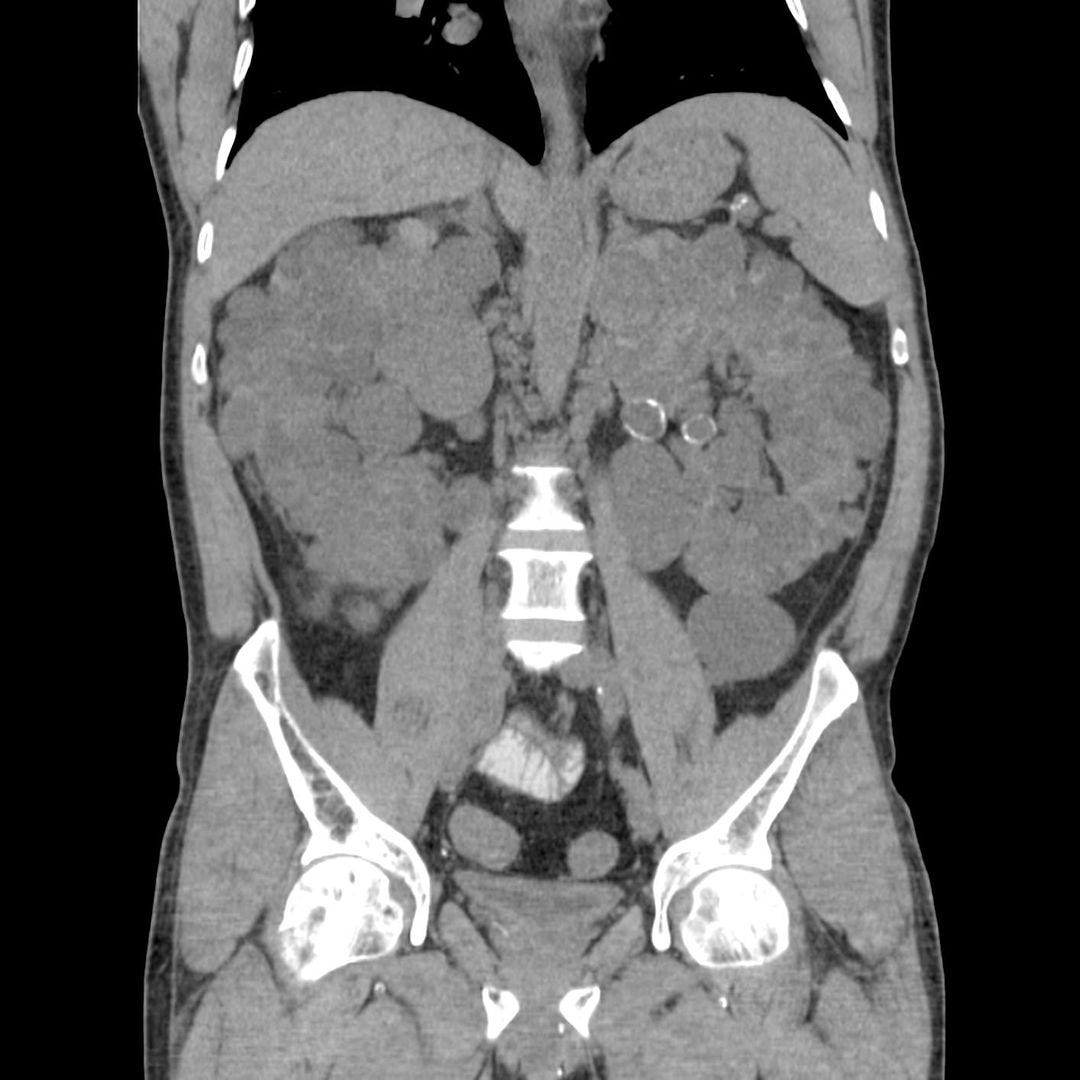
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPCKD) is a common inherited condition in which epithelial lined cysts form in the kidneys and destroy normal parenchyma leading to early hypertension and progressive renal dysfunction. Flank or back pain is present in ~ 60% of patients and may be due to the enlarged kidneys pressing on adjacent structures, intracyst hemorrhage, or infection. Renal failure occurs in 30-50% and usually manifests by the fifth or sixth decades.
Associated imaging findings include nephrolithiasis, pancreatic and hepatic cysts, intracranial aneurysms ( in ~ 10%), colonic diverticula and cardiac valve abnormalities. When intracranial aneurysms are seen in ADPKD they typically involve the middle cerebral artery and are often larger than aneurysms unrelated to ADPCKD.